2017年IOAA理论第9题-星系物质外流
英文原题
Galactic Outflow [20 marks]
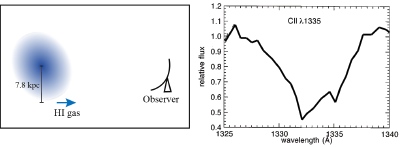
Cannon et al. (2004) conducted an HI observation of a disk starburst galaxy, IRAS 0833+6517, with the Very Large Array (VLA). The galaxy is located at a distance of 80.2 Mpc with an approximate inclination angle of 23 degrees. According to the HI velocity map, IRAS 0833+6517 appears to be undergoing regular rotation with an observed radial velocity of the HI gas of roughly 5850 km s^-1 at a distance of 7.8 kpc from the centre (the left panel of the figure below).
Gas outflow from IRAS 0833+6517 is traced by using the blueshifted interstellar absorption lines observed against the backlight of the stellar continuum (the right panel of the figure). Assuming that this galaxy is gravitationally stable and all the stars are moving in circular orbits,
a) Determine the rotational velocity (v_rot) of IRAS 0833+6517 at the observed radius of HI gas. [5]
b) Calculate the escape velocity for a test particle in the gas outflow at the radius of 7.8 kpc. [9]
c) Determine if the outflowing gas can escape from the galaxy at this radius by considering the velocity offset of the C IIλ1335 absorption line, which is already corrected for the cosmological recessional velocity. (The central rest-frame wavelength of the CII absorption line is 1335 Å.) (YES / NO) [6]