“2020年GeCAA理论第8题-木星大红斑”的版本间的差异
(创建页面,内容为“有框|居中 In the following problem the fluid mechanics of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot (GRS) is studied based on the velo…”) |
(没有差异)
|
2024年4月14日 (日) 15:59的版本
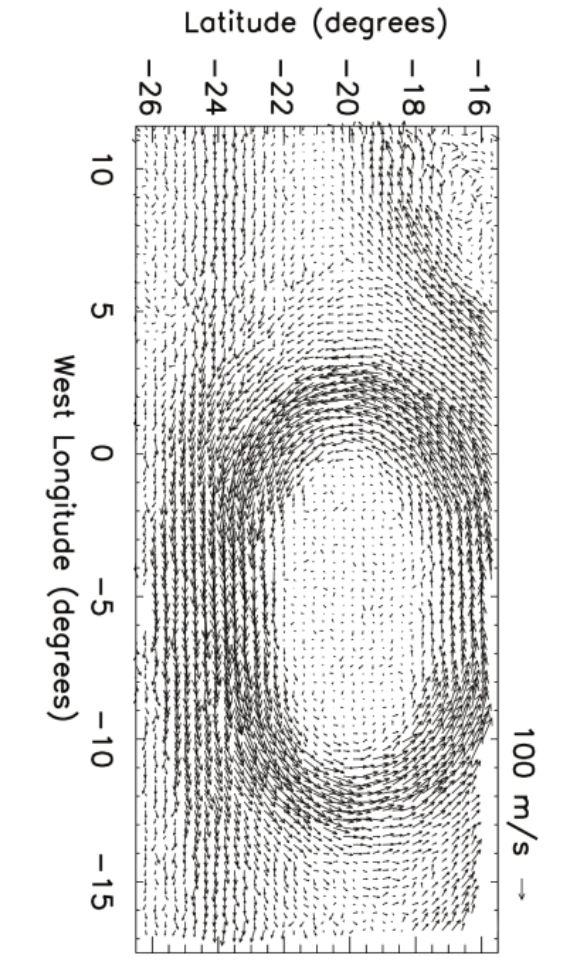
In the following problem the fluid mechanics of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot (GRS) is studied based on the velocity field data. The diagram on the next page shows a map of relative velocity for GRS and the surrounding region. The arrows are oriented and scaled as per the directions and magnitudes of winds at different points.
Due to the combined effects of gravity and rotation, Jupiter is slightly flattened at its poles. The equation of a spheroid approximating for the shape of Jupiter can be stated as:
$$\frac{x^{2} +y^{2} }{R_{e}^{2} } +\frac{z^{2} }{R_{p}^{2}} =1$$
where $$R_{e}=7.15\times 10^{7} m$$ is the equatorial radius of Jupiter, and $$R_{p}=6.69\times 10^{7}m$$ the polar radius. The radii of curvature of this spheroid in any direction can be calculated by the following equations $$(\epsilon =\frac{R_{e}}{R_{p}} )$$: